Table of Contents
Electric fuses have protected homes from excessive current flows and system temperature increases. They are still found in older homes and are often code compliant. Read on to find more about everything you need to know about electric fuses.
What is an Electrical Fuse?
Electric fuses eliminate potential dangers like excessive temperatures and power surges to the electrical systems. Fuses are intentionally placed in a circuit as a weak point so that it is sacrificed during a high current from an overloaded or short circuit by melting it and breaking the circuit.
What is a Fuse Box?
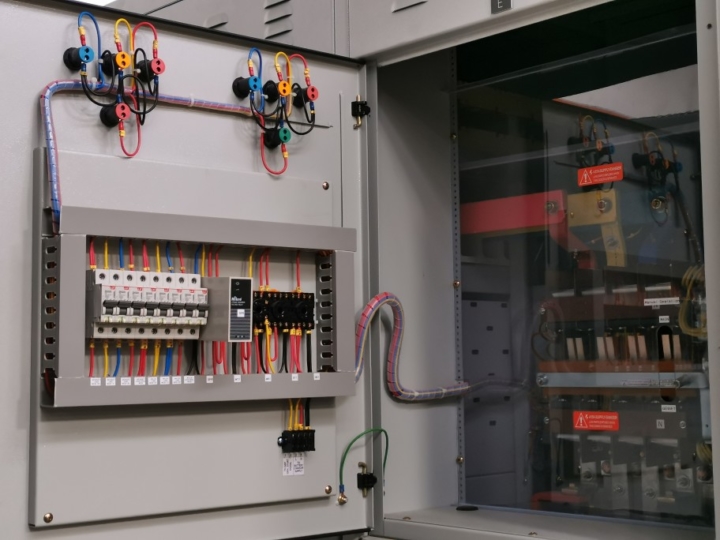
The fuse box is a metal box which acts as a central hub of the electrical system where the incoming voltage is separated into the various circuits. Also known as a service panel, breaker panel, or junction box, this central switchboard supplies power to every electrical system in your home.
It contains between six to twelve screw-in fuses and cartridge fuses. Older fuse boxes had a 60-amp total capacity. But today, most residential electrical systems have a 200-amp total capacity.
How Does a Fuse Work?
A fuse is an Overcurrent Protective Device (OCPD), as classified by the National Electrical Code. For a fuse to work efficiently, it must contain a fusible section, which is a piece capable of melting. This is known as a fusing element made of a metal strip sealed inside a glass fuse body.
When the fuse element receives more power than it can handle, it heats and melts. The circuit breaks, rendering that the circuit is finished and safe. Once this happens, the fuse needs to be replaced with a new one.
What is the Difference Between Circuit Breaker and Fuse?
Since fuse is also used as an OCPD, it is often put in the same category as a circuit breaker. But they are not the same products! The main difference between Circuit Breaker and Fuse lies that a circuit breaker can be reused again, but a fuse cannot. Fuses protect your home and devices against overloading. While circuit breakers protect your home against overloading and short-circuits.
What Are the Different Types of Fuse?
The correct fuse box will prevent house fires and damage to your house. There are three styles of fuses you can see today:
- Type-T (Edison base) Fuses: These are standard fuses used for almost every 120 to 125-volt household circuit.
- Type-S (Rejection base) Fuses: These types of fuses contain fuse and an adapter that can fit inside an Edison-type socket.
- Cartridge Fuses: These fuses are used for 240-volt appliance circuits, controlling the power of the fuse box.
Why Do Fuses Blow?
Fuses can blow for several reasons, such as:
- Overload Fuse Blows: Sometimes electric overload that is six times more than the normal current flow can cause the circuit to open and the fuse to blow. Overloads generally happen when too many devices are plugged into the same circuit.
- Short Circuit Fuse Blows: Short circuits are caused when a low-resistance electricity path receives a high-volume current. If a nail or screw pierces electric cables, water can enter the electrical box and cause a short circuit. They are thousand times greater than the normal current that can melt metal, cause arch fires, damage wire insulations, and vaporize conductors.
- Ground Fault Fuse Blows: When a powered hot wire touches anything grounded like a metal pipe, electrical box, your hand, a bare ground wire, or an outlet, it results in a ground fault causing the electric fuse to blow.
How To Know a Fuse is Blown?
Either visually or with the help of a device called a continuity tester or ohmmeter, you can know whether a fuse has blown.
- Visual Testing: If the glass window on screw-in fuses is clear, you will be able to see whether the fusing element inside the box is severed. It may appear brown, cloudy, or black because of the melting fusing element.
- Testing Device: With the help of devices such as ohmmeter and continuity testers, you can measure electrical resistance. For checking a screw-in fuse, keep one test lead to the end of the fuse and the other to the threaded side. Hold the test leads at opposite ends of the fuse to check whether the current is flowing through the fuse for the cartridge fuse.
How To Change a Fuse in a Fuse Box?
To change a fuse in a fuse box, you will need appliances such as an electrical testing device like an ohmmeter or a continuity test, a flashlight, a screw-in fuse replacement, and a cartridge fuse replacement. You can read in detail about how to do it change a fuse here.