Table of Contents
What are Molded Case Circuit Breakers(MCCB)?
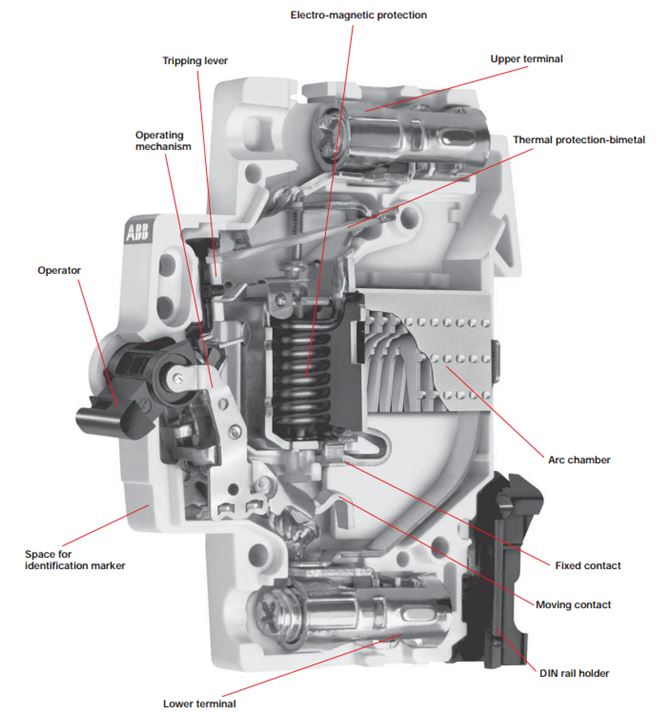
Molded Case Circuit Breakers(MCCB) are electrical protection gadgets that can be used with a wide range of voltages to protect your appliances and electrical circuit from excessive current. MCCBs, as they are commonly known, have adjustable trip settings and can hold as much as 2,500 amps in current ratings. They are also used with frequencies that are 50 and 60 Hz and have the following 3 functions:
- They offer protection in case of electrical faults by immediately interrupting a current that is extremely high due to a line fault or a short circuit.
- They protect in the event of an overload where the current is higher than the rated value and lasts a longer time than normal.
- The on and off function can be used to switch the circuit on or off for repairs and replacements.
Applications of MCCB (Molded Case Circuit Breakers)
Due to the fact that they can handle especially high currents, molded case circuit breakers are often used with applications that are heavy duty. Some of the applications of MMCB are as follows:
-
Protecting Generators
They usually produce hundreds of amps in output and require expensive gen-sets. MCCBs, which can handle the current ratings, provide the protection needed.
-
Protecting Electric Feeders
If you are using feeder circuits to distribute electric current, they can carry hundreds of amps. In some instances, you may also have additional circuits that will need trip settings. MCCBs come in handy in both the situations.
-
Welding Machines
It is possible to have some welding applications that draw very high currents thus needing MCCBs since miniature circuit breakers cannot handle the high currents.
-
Protecting Capacitor Banks
These are used to correct power factors in industrial and commercial electrical systems. If the currents they draw are very high, MCCB protection becomes a necessity to reduce currents.
-
Protecting Motors
Electric motors also need to be adequately protected and MCCBs do this work very well. Inrush current may need to be adjusted, providing the necessary overload protection without tripping.
-
Adjustable trip settings for applications with low currents
MCCBs, even though they are known to be used with high current applications can also be used with low current ones. They provide adjustable trip settings.
-
Thermal Protection
This is where you use an over-current about 300 percent above the rated value. Ideally, the breaker should trip correctly. If it doesn’t then it is failing in thermal protection.
-
Magnetic Protection
Here you would want to simulate a fault by sending pulses of current that are very high. The pulses need to be very short since a fault can be very dangerous. Magnetic protection tends to be instant and these can be handled well by the application.
- A visual inspection
- Cleaning
- Lubrication
- Testing as explained in the section above
- Electric arcing indicated by casing or contact burns
- Signs of overheating such as insulation and casing cracks or deformed contacts
How to test a MCCBs?
Testing Insulation Resistance
This test is done to ensure that you get reliable protection. It requires you to disconnect the MCCB so that you can test the insulation across the load terminals, supply terminals and between phases. If the insulation resistance is found to be lower than the manufacturers’ recommended value, then the protection is not adequate.
Testing Contact Resistance
Usually, this is a rather low value because the MCCB needs to allow current to pass through even when it has a low voltage. You will need to test the resistance of electrical contact and then compare your findings with the manufacturer’s recommendations.
The Tripping Test
You will need to simulate a fault or overcurrent and then observe how the MCCB responds. You want to carry out this test last since the MCCB will heat up due to the high current. It is a two-part test which is conducted in the following sequence:
Maintaining MCCBs
It is important to periodically provide maintenance for your molded case circuit breakers if they are to provide reliable protection. Some of the maintenance procedures necessary include the following:
Carrying Out a Visual Inspection
This simply means checking for any signs that the MCCB has been damaged. Some of the signs that indicate damage include the following:
There are MCCBs that are sealed at the factory and others that can be opened. If yours can be opened, take a look at its internal components.
Cleaning
Dirt accumulated over time, can cause the components of the MCCB to deteriorate. Additionally, dirt can conduct electricity and cause a fault internally. Use a vacuum cleaner to get rid of the dirt. With the dirt removed, even your visual inspection becomes much easier.
Lubrication
As mentioned above, there are MCCBs that are sealed at the factory and others that can be opened. Lubrication is only applicable to those that can be opened. It ensures that moving parts and the manual disconnection switch work properly. This is a critical factor where faults are concerned.
Conclusion
High current applications need to have molded case circuit breakers. Getting the right size and ensuring that proper maintenance is carried out means that you will have a reliable MCCB that is also safe. To find out more about MCCBs, contact us here and we will be happy to give you more information.